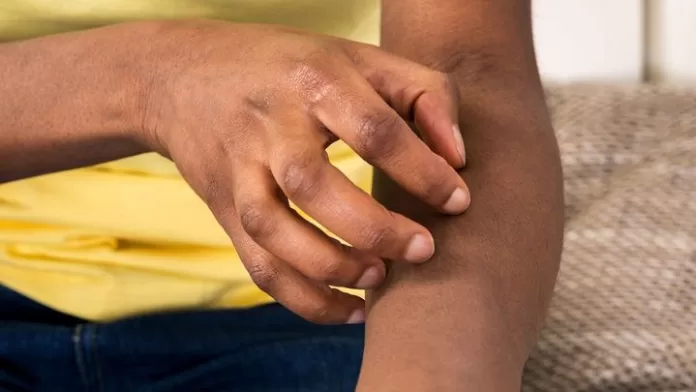
Diabetes doesn’t just affect your blood sugar levels – it can also have a significant impact on your skin. People with diabetes are at a higher risk for various skin issues, and this is often due to the way high blood sugar levels can interfere with the body’s ability to heal and protect itself. From dry skin to infections, understanding how diabetes affects your skin is essential for maintaining both your skin and overall health. Here’s a closer look at the effects and how you can protect your skin.
1. Dry Skin
One of the most common skin issues for people with diabetes is dry skin. High blood sugar levels lead to dehydration because the kidneys work overtime to remove excess sugar through urine. This causes the skin to lose moisture and become dry, flaky, and itchy. Over time, dry skin can crack, making it more vulnerable to infections. The best way to combat this is by moisturizing regularly with a thick, fragrance-free cream or lotion. Additionally, drinking plenty of water helps keep your skin hydrated from the inside out.
2. Diabetic Dermopathy
Diabetic dermopathy refers to the appearance of brown, scaly patches on the skin, usually on the lower legs. It’s a harmless condition but can be a sign of poor blood circulation related to diabetes. Managing your blood sugar levels effectively is key to preventing and managing diabetic dermopathy. Additionally, sun exposure can worsen the appearance of these patches, so it’s important to use sunscreen on affected areas to prevent further skin damage.
3. Infections
High blood sugar weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. People with diabetes are more prone to both bacterial and fungal infections, particularly in areas where the skin rubs together, such as under the arms, in the groin, or between the toes. Keeping your skin clean and dry is essential to avoid infections. After bathing, make sure to thoroughly dry these areas and consider using an antifungal cream if you experience any irritation or signs of infection. Early treatment can help prevent complications.
4. Poor Wound Healing
One of the more frustrating side effects of diabetes is poor wound healing. Even small cuts and scrapes can take longer to heal due to impaired blood flow and the body’s inability to properly repair tissue. This makes people with diabetes more susceptible to infections, especially in the feet. It’s important to inspect your skin regularly, particularly your feet, for cuts, blisters, or sores. When wounds do appear, clean them properly, apply an antiseptic, and cover them with a bandage. If a wound is not healing, seek medical attention immediately to prevent further complications.
5. Acanthosis Nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans is a condition that causes dark, velvety patches of skin, often on the back of the neck, armpits, or groin. It is linked to insulin resistance, a common issue for people with Type 2 diabetes. While not harmful, it can be a sign that diabetes isn’t well-controlled. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels can help reduce or prevent the appearance of these patches. In some cases, your doctor may recommend treatments such as topical creams to improve the skin’s appearance.
READ ALSO: 10 Benefits of Planting Early in Rainy Season
6. Skin Tags
Skin tags are another skin condition that’s more common in people with diabetes. These are small, soft growths that typically form in areas where skin rubs together, such as the neck, armpits, or under the breasts. While skin tags are generally harmless, they can become irritated or painful if they get caught on clothing or jewelry. Regularly checking your skin can help you identify skin tags early. If they become bothersome, your healthcare provider can remove them safely.
7. Psoriasis and Eczema
People with diabetes may also experience flare-ups of inflammatory skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema. These conditions cause redness, irritation, and scaling of the skin, and they can be more frequent in individuals with diabetes, especially if blood sugar levels are poorly controlled. Managing stress, using mild skincare products, and keeping blood sugar levels stable can help reduce flare-ups. If you suffer from these conditions, it’s worth discussing treatment options with your doctor to keep them under control.
Final Thoughts
Diabetes can lead to a range of skin problems, but with proper care, many of these issues can be prevented or managed. Moisturizing regularly, staying hydrated, and maintaining good blood sugar control are all essential steps in protecting your skin. It’s also important to inspect your skin frequently for any changes or issues, especially in areas like your feet. If you notice slow-healing wounds, skin tags, or unusual changes in your skin, consult your doctor for advice and treatment. By taking proactive steps, you can protect your skin and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.